Make a geodetic New Year’s resolution: stop making basic positioning mistakes!
This New Year, why not resolve to stop making basic geodetic positioning mistakes in your ArcGIS documents. We’re sure your boss, customers and organisation will thank you.
![]() To help you with this, Exprodat and Priemere GeoTechnology have collaborated to create a free tool, called the Geodetic Assistant – an ArcGIS extension that uses the EPSG Area Polygons dataset to check for and help you fix any coordinate reference system (CRS) and coordinate transformation problems.
To help you with this, Exprodat and Priemere GeoTechnology have collaborated to create a free tool, called the Geodetic Assistant – an ArcGIS extension that uses the EPSG Area Polygons dataset to check for and help you fix any coordinate reference system (CRS) and coordinate transformation problems.

The Geodetic Assistant is simple to use, and helps you avoid some of the main spatial reference pitfalls such as not setting a coordinate transformation. Alerts will notify you when problems are detected, and the main interface provides further information on issues and allows you to quickly fix any issues.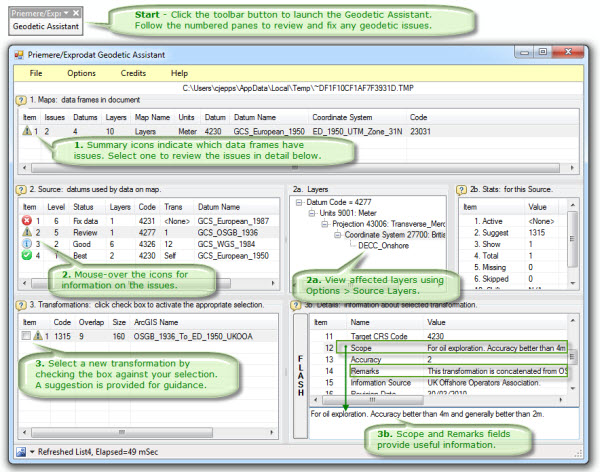
Bottom line – if you are working with multiple geodetic datums and not applying coordinate transformations in your ArcMap session, you probably should be. Fix this by using the Geodetic Assistant to help you decide the most suitable coordinate transformations to apply.
Why should I bother?
The OGP has publicised cases * where geodetic mistakes have led to minor differences in position great enough that…
- wells were mistakenly drilled in the wrong lease,
- wells missed their target due to incorrect geosteering,
- wells intersected adjacent boreholes because they were positioned incorrectly,
- seismic had to be re-processed due to positioning errors in original processing.
As you can imagine, such errors can be extremely costly, not to mention dangerous for workers and catastrophic for company reputation. From our experience, we believe many ArcGIS users in the petroleum industry are unknowingly making similar subtle mistakes on a regular basis.
Here’s the science bit…
All spatial data in a GIS has coordinates. Coordinates belong to a coordinate system (CS). A CS describes the mathematical rules governing the coordinate space, e.g. axes, direction, units, etc. When coordinates are used to describe position on the Earth, they belong to a coordinate reference system (CRS).
A CRS is a CS referenced to the earth. This referencing is achieved through the use of a geodetic datum – an ellipsoid either referenced to a specific known point on the Earth or Earth-centred (derived through satellite measurements). Geodetic surveyors use a mathematic model of the Earth for their calculations – many models exist, each with variations in origin, size, shape, orientation and scale relative to the Earth. This leads to many different CRSs, referencing many different geodetic datums. *
If you’d like to learn more, why not attend Exprodat’s ArcGIS Coordinate Reference Systems for Petroleum training course?
Here’s the issue…
ArcGIS comes “fully loaded” with tools for correctly using and managing these CRS and coordinate transformations, but leaves the decision on how these are employed up to you, the user.
From our work with oil and gas companies, we often see users handling geodetic issues incorrectly, or worse still, ignoring them altogether – this is possibly the worst thing you can do as not setting relevant coordinate transformations at all can result in large positioning errors (e.g. hundreds of metres).
There is hope…
The Geodetic Assistant can help you identify and fix these issues, as well as monitor what you are doing in ArcGIS and alert you when problems occur.
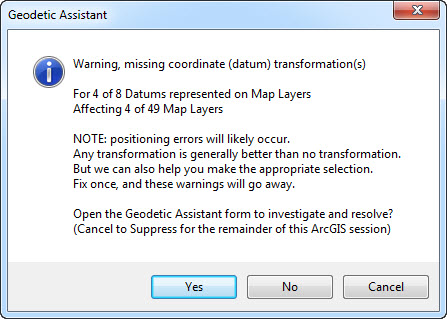
So, this New Year, do yourself and your organisation a favour and check out the free Geodetic Assistant to help stop making basic geodetic errors, it’ll be the best New Year’s resolution you ever made.
Posted by Chris Jepps, Technical Director, Exprodat, and Rich Priem, Priemere GeoTechnology.
PS – Geodetics is a complex subject, and the user has ultimate responsibility for maintaining spatial integrity. If in doubt, consult an expert!
Additional Credits:
- OGP – much of this information based on the OGP Geodetic awareness guidance note. *






